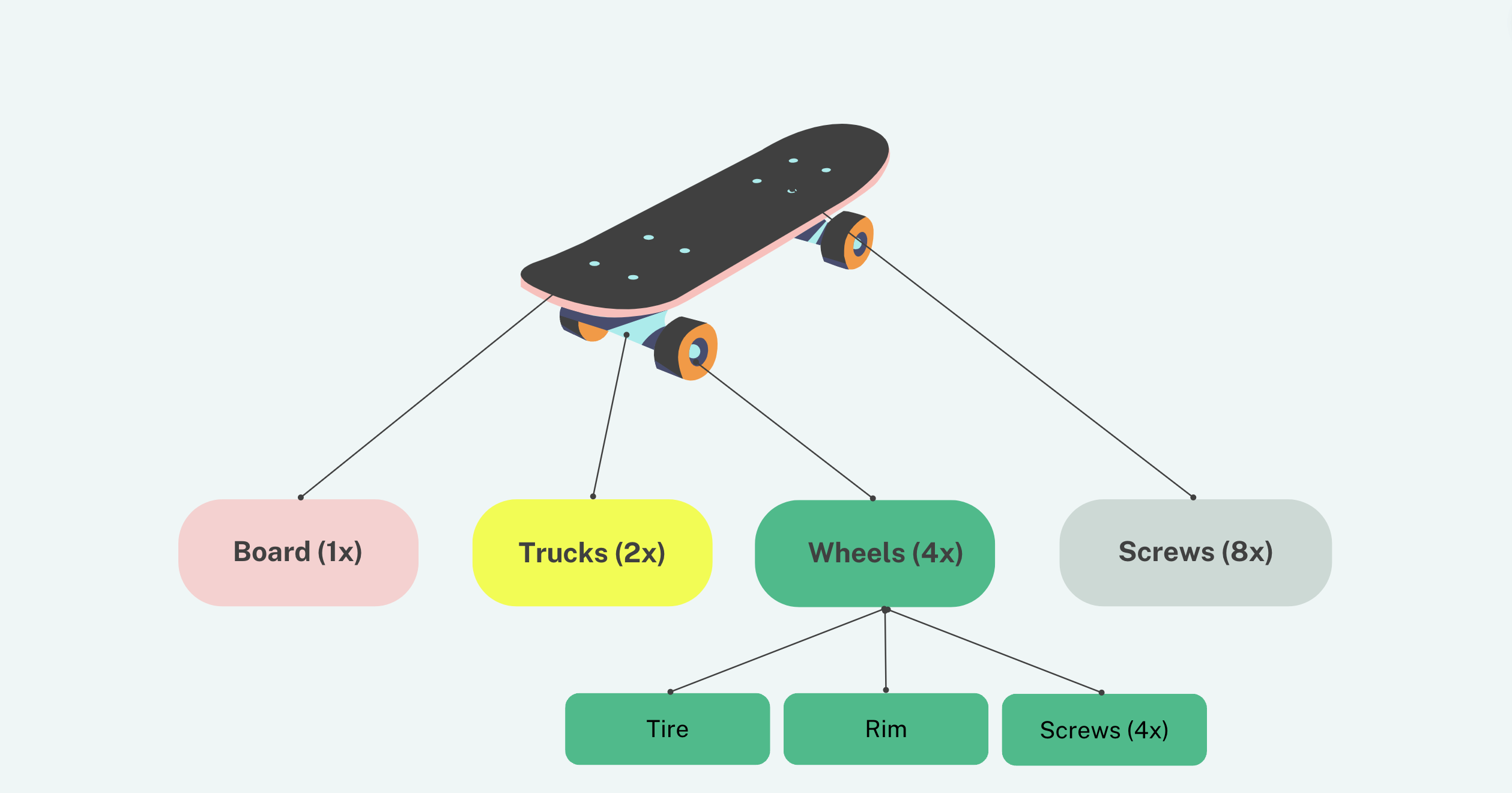
A Bill of Materials (BOM) is a comprehensive list of parts, items, assemblies, and other materials required to create a product, as well as the instructions needed to gather and use the materials. Think of it as the recipe for a product, where each ingredient and its quantity are meticulously listed to ensure the final product is made correctly.
A BOM serves as a critical reference for anyone involved in the manufacturing process, from engineers and designers to purchasing and production teams. It ensures everyone is on the same page and helps streamline the production process, manage inventory, and reduce errors.
Types of Bill of Materials
- Engineering BOM (EBOM): Created by engineers during the product design phase, the EBOM lists the components and assemblies designed by the engineering team. It focuses on the technical and functional aspects of the product.
- Manufacturing BOM (MBOM): The MBOM is used during the manufacturing process and includes details on the components required for assembly, including raw materials and subassemblies. It often incorporates additional information such as the order of assembly and required tooling.
- Sales BOM (SBOM): The SBOM is used for sales purposes, detailing the product from a sales perspective. It lists the finished product and components that may be required for sales configuration.
Components of a BOM
A typical BOM includes the following elements:
- Part Number: A unique identifier assigned to each component.
- Part Name: The name or description of the component.
- Quantity: The number of each component required.
- Unit of Measure: The unit used to quantify each component (e.g., pieces, kilograms).
- Description: A detailed description of the component.
- Procurement Type: Indicates whether the component is purchased or manufactured in-house.
- Reference Designators: Used in electronic BOMs to identify the location of components on circuit boards.
- Assembly Instructions: Step-by-step instructions for assembling the components.
Creating a Bill of Materials
Let’s create a simple BOM for a hypothetical product: a basic wooden table.
Product: Wooden Table
| Item No. | Part Number | Part Name | Quantity | Unit of Measure | Description | Procurement Type | Assembly Instructions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 001 | Tabletop | 1 | Piece | 120cm x 60cm rectangular wooden board | Purchase | Attach legs to each corner |
| 2 | 002 | Table Leg | 4 | Pieces | 75cm wooden legs | Manufacture | Secure to tabletop with screws |
| 3 | 003 | Screw | 16 | Pieces | 5cm wood screws | Purchase | Use for securing legs to tabletop |
| 4 | 004 | Wood Finish | 1 | Can | 500ml wood varnish | Purchase | Apply evenly to the tabletop surface |
| 5 | 005 | Sandpaper | 2 | Pieces | Medium grit sandpaper sheets | Purchase | Sand tabletop before applying finish |
Conclusion
A Bill of Materials is a foundational document in the manufacturing process, providing detailed information about the materials, components, and instructions needed to create a product. It ensures accuracy, efficiency, and consistency, making it an indispensable tool for engineers, manufacturers, and purchasing teams alike. Whether you’re creating a simple wooden table or a complex electronic device, a well-prepared BOM is crucial for successful product development and manufacturing.